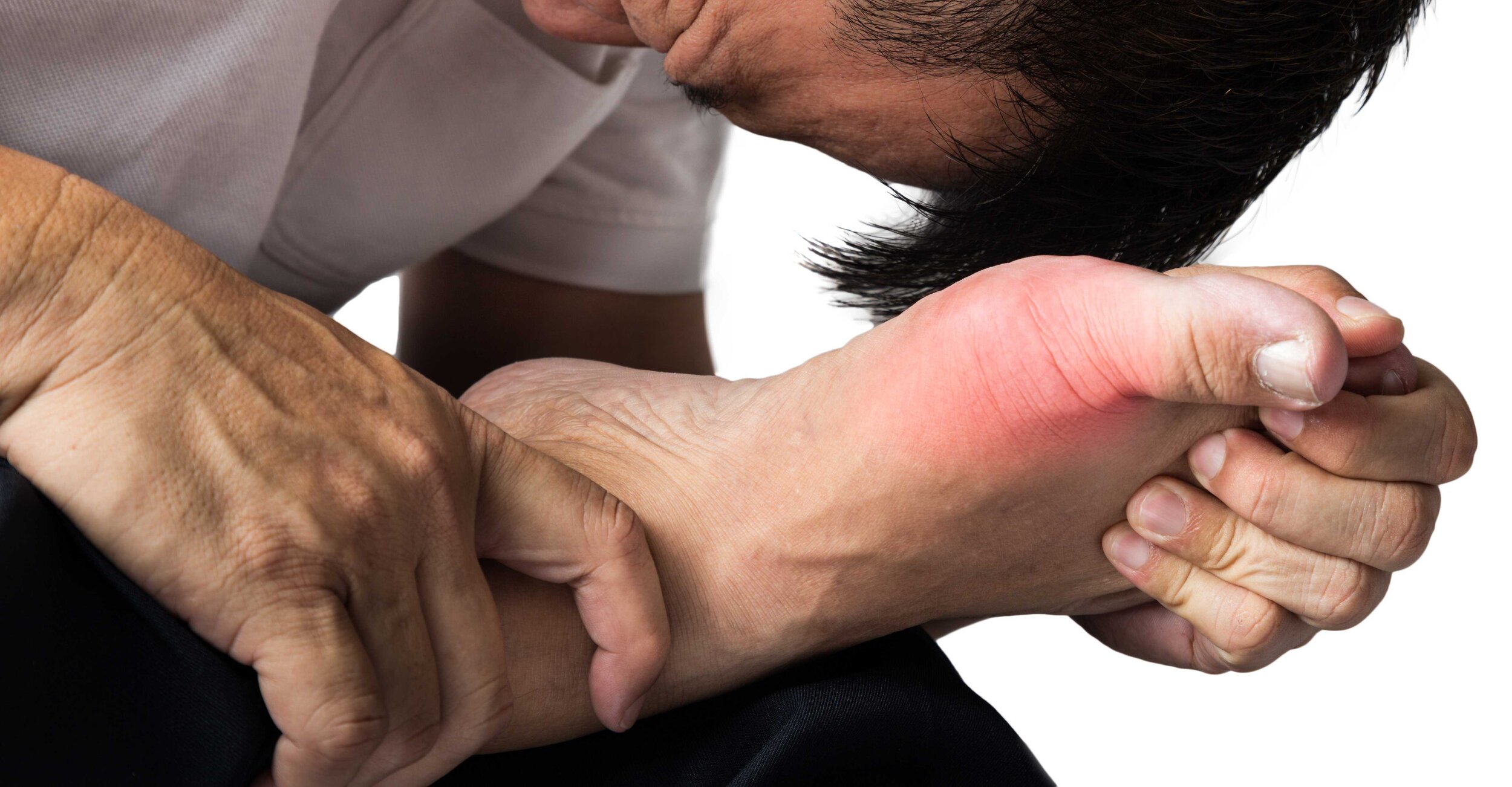
Gout
Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs due to a build of up uric acid in the body and joint fluid (hyperuricemia). This accumulation typical occurs when a body has difficulty processing certain protein substances called purines that are found naturally in the body. This excess can result when the body produces too much uric acid or has difficulty eliminating uric acid. Gout is typically hereditary and most commonly presents in males between 50 and 60 years of age.
Signs and Symptoms
Sudden onset of intense pain in one or more joints, the great toe joint is the most commonly affected
Redness
Swelling
Warmth over the joint
No injury can be recalled
Pain with activity and shoe gear
Diagnose and Treatment
Diagnosis of gout is revealed from history and physical examination findings with x-rays and bloodwork often used as confirmation.
Treatment is geared toward fast pain relief, involving the use of anti-inflammatories. Chronic gout can be controlled with medication and lifestyle changes. Avoiding foods that are high in purines will reduce the frequency of gout attacks. These foods include red meat, shell fish, beer, red wine and salt.